O-arm™
Surgical imaging system
For Spine, Orthopaedic Trauma, and Neurological Procedures

The O-arm™ system is an intraoperative 2D/3D imaging system that is designed to meet the workflow demands of the surgical environment. It can be used in variety of procedures including spine, cranial, and orthopedics.
O-arm™ is part of the AiBLE™ solution
O-arm™ Surgical Imaging System is a foundational component of AiBLE™, Medtronic's digital data-driven surgery ecosystem.
AiBLE™ is an integrated experience of innovative technology, software, services and people that aims to Connect, Predict and Advance.
O-arm™ 4.3 software - now available in India
Medtronic surgical imaging has reached new levels.
Introducing 3 new functional enhancements: 3D Long Scan, Spine Smart Dose and Medtronic Implant Resolution.
3D Long Scan (3DLS), with robotic gantry movement, now allows 3D imaging up to 43.8cm, adding visibility to additional levels of the patients spinal anatomy.8
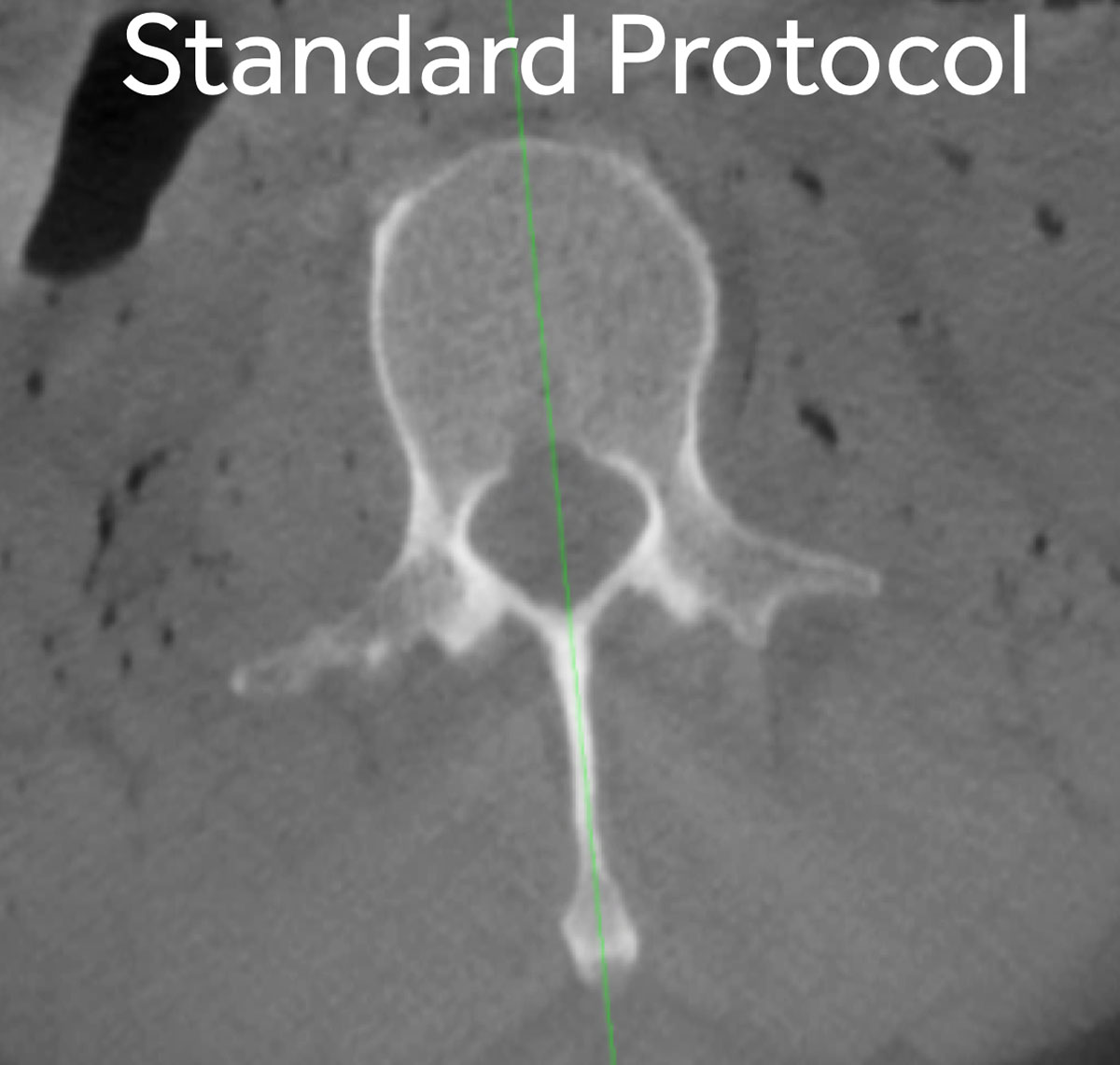
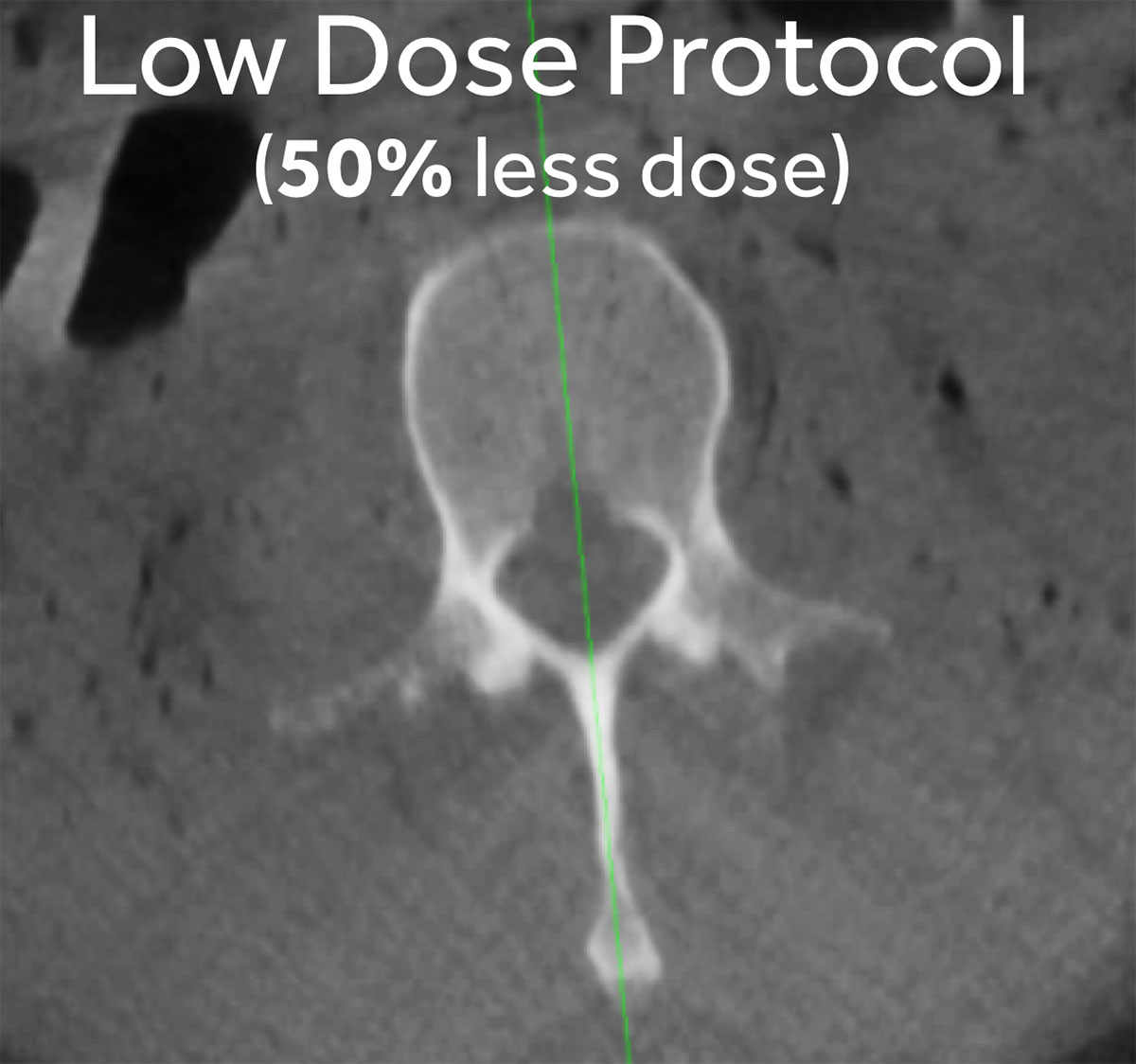
The Spine Smart Dose (SSD), an AI based algorithm, only needs 70% of the dose of a standard scan, while maintaining the image quality.8

Standard Dose

Spine Smart Dose
To support surgeons in making a confident clinical decision, the new Medtronic Implant Resolution (MIR) functionality aids. It helps with evaluation of the screw placement by enhancing the visualization of the bone anatomy around certain Medtronic screw systems.8
Indications
The O-arm™ O2 Imaging System is a mobile x-ray system designed for 2D fluoroscopic and 3D imaging for adult and pediatric patients weighing 27kg or greater and having an abdominal thickness greater than 16cm, and is intended to be used where a physician benefits from 2D and 3D information of anatomic structures and objects with high x-ray attenuation such as bony anatomy and metallic objects. The O-arm™ O2 Imaging System is compatible with certain image guided surgery systems.
Product details
The O-arm™ system’s high quality, versatile imaging provides the information you need to guide your clinical decision making.
Advanced energy solutions
Along with StealthStation navigation, the O-arm™ system provides enhanced 3D visibility and surgical feedback. It also:
- Provides current patient data in the OR
- Enables advanced surgical approaches like MIS
- Provides additional information in challenging procedures, like heavier patients or patients with unusual anatomy1,2,3
- Automatic registration keeps the process simple
The O-arm™ system also offers options for workflow efficiencies, such as:
- In procedures where pre-op axial/coronal/sagittal slice data is necessary, it may be possible to use the O-arm™ system to provide the initial data set
- Eliminating the need to send patients to be scanned in radiology

Imaging protocols
The O-arm™ system provides flexibility for surgeons to achieve As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA). Multiple image protocols allow the surgeon flexibility to choose the appropriate dose to the patient based upon individual clinical objectives.4
Opportunities to reduce dose
With opportunities to reduce dose to the surgeon and staff, the O-arm™ and StealthStation systems eliminate the need to wear lead protective apparel during the navigated steps of the procedure.5,6
Surgical workflow
The O-arm™ system has been designed to complement the surgical workflow with:
- Multiple surgical table options
- Inter-room mobility for concurrent cases
- On-demand imaging, no need to schedule in advance
Technical specifications
| Category |
Specification |
|
|---|---|---|
| Physical dimensions |
Length |
252 cm gantry door open |
| Width |
81.3 cm |
|
| Height |
198 cm gantry door closed (can be lowered) |
|
| Weight |
885kg approx. |
|
| Gantry Opening |
69.9 cm |
|
| Bore Diameter |
96.5 cm |
|
References
Kovanda TJ, Ansari SF, Qaiser R, Fulkerson DH. Feasibility of CT-based intraoperative 3D stereotactic image-guided navigation in the upper cervical spine of children 10 years of age or younger: initial experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015;16(5):1-9.
™Liu Y, Li X, Sun H, Yang H, Jiang W. Transpedicular wedge osteotomy for treatment of kyphosis after L1 fracture using intraoperative, full rotation, three-dimensional image (O-arm™)-based navigation: a case report. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):18889-18893.
Houten JK, Nasser R, Baxi N. Clinical assessment of percutaneous lumbar pedicle screw placement using the O-arm™ multidimensional surgical imaging system. Neurosurgery. 2012 Apr; 70(4):990-5
Dosimetry_Report_O2_BI-160-00227_Rev_2
Nottmeier E.W., Bowman C., Nelson K.L. Surgeon radiation exposure in cone beam computed tomography-based, image-guided spinal surgery. Int J Med Robot. 2012 Jun;8(2):196-200
Pitteloud N, Gamulin A, Barea C, Damet J, Racloz G, Sans-Merce M. Radiation exposure using the O-arm™ surgical imaging system. European Spine Journal JO - Eur Spine J. 2017;26(3):651-657.
Medtronic internal document: 10501 O-arm™ Journal Database - All Applications Q4FY21
Medtronic internal document: O-arm™ 4.3 Claims matrix
Van de Kelft E, Costa F, Van der Planken D, Schils F. A Prospective Multicenter Registry on the Accuracy of Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracic, Lumbar, and Sacral Levels With the Use of the O-arm™ Imaging System and StealthStation Navigation. Spine 2012;37(25):E1580-7.
Burch S, et al. Comparison of radiation exposure to the spine surgeon during pedicle screw placement using the O-arm™ System and StealthStation Navigation vs. C-arm Standard fluoroscopy. 2010
Silbermann J, Riese F, Allam Y, Reichert T, Koeppert H, GutberletM. Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in lumbar and sacral spine: comparison between free-hand and O-arm™ based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J 2011;20(6):875-81.
Shin MH, Ryu KS, Park CK. Accuracy and safety in pedicle screw placement in the thoracic and lumbar spines: Comparison study between conventional C-arm fluoroscopy and navigation coupled with O-arm™ (registered trademark) guided methods. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2012;52(3):204-9.
Allam Y, Silbermann J, Riese F, Greiner-Perth R. Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in thoracic spine: comparison between free hand and a generic 3D-based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J 2013;22:648-53
Shin, M.-H., Hur, J.-W., Ryu, K.-S., & Park, C.-K. Prospective Comparison Study between the Fluoroscopy-guided and Navigation Coupled with O-arm™ -Guided Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracic and Lumbosacral Spines. Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques. 2015. 28(6), E347–E351.
Verma, S. K., Singh, P. K., Agrawal, D., Sinha, S., Gupta, D., Satyarthee, G. D., & Sharma, B. S. (2016). O-arm™ with navigation versus C-arm: a reviewof screw placement over 3 years at a major trauma center. British Journal of Neurosurgery, 1–4.
Dea, N., Fisher, C. G., Batke, J., Strelzow, J., Mendelsohn, D., Paquette, S. J., … Street, J. T. (2016). Economic evaluation comparing intraoperative cone beamCT-based navigation and conventional fluoroscopy for the placement of spinal pedicle screws: A patient-level data cost-effectiveness analysis. Spine Journal, 16(1), 23–3
