Imagine what you can do with a fully-connected surgical suite.
Discover a unified suite of surgical technologies from Medtronic — designed to shift the way we imagine and deliver spine care, both inside and outside the OR.
Meet the AiBLE™ surgical ecosystem.
A suite of navigation, imaging, guidance, planning, and AI technologies that enable you to perform more predictable procedures in the OR.
Therapies and procedures
Vertebral augmentation
Restoring height and relieving pain.1
Learn about procedures that treat pain caused by vertebral compression fractures and the products that can help.

Oblique lateral interbody fusion (OLIF)
Learn about OLIF25™, a psoas-preserving approach to the L2-L5 disc spaces, and OLIF51™, a laterally-positioned ALIF approach to the L5-S1 disc spaces.
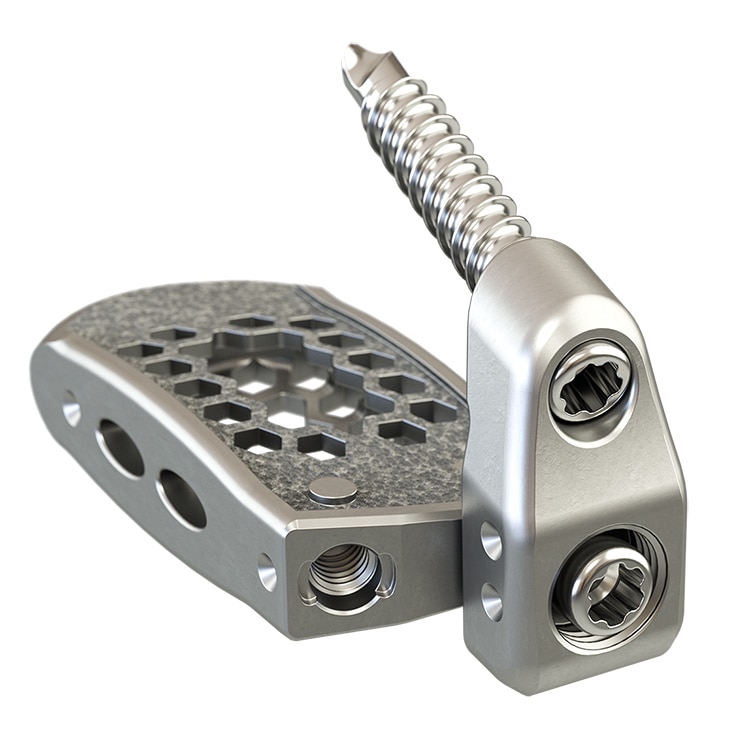
Interbody cages and bone grafts
Find out more about interbody cages and proprietary surface technologies for a wide range of patient needs. Learn about the biologics that set Medtronic spinal fusions apart.

The Medtronic ecosystem of minimally invasive solutions (MIS)
Meet the Medtronic minimally invasive solutions (MIS) portfolio for spine surgery, blending AI-powered data, robotics, navigation, implants, and more.
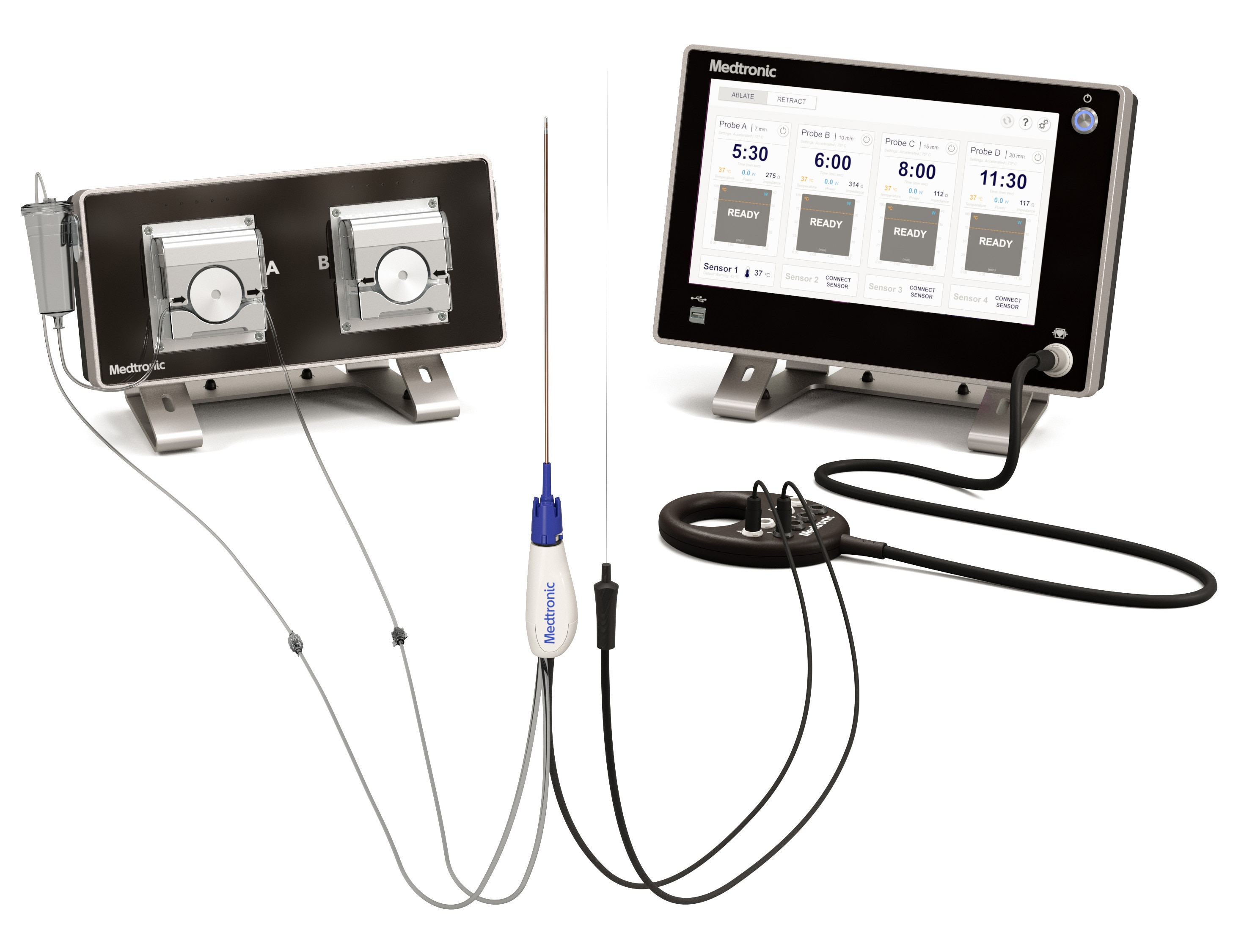
Radiofrequency (RF) ablation for bone tumors
The OsteoCool™ 2.0 system is an internally-cooled RF ablation system with four-probe capability to palliatively treat painful bone tumors.

Education, training, and events
Explore courses, videos, and educational opportunities for spine surgeons at all stages of their careers.
Products
- Van Meirhaeghe J, Bastian L, Boonen S, et al. A randomized trial of balloon kyphoplasty and nonsurgical management for treating acute vertebral compression fractures: vertebral body kyphosis correction and surgical parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(12):971–983.
