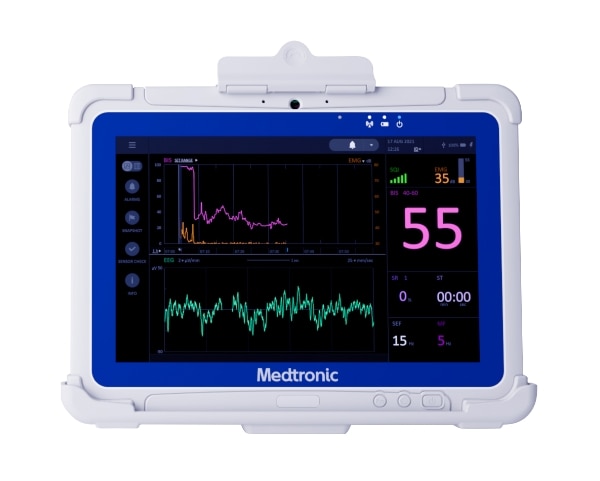
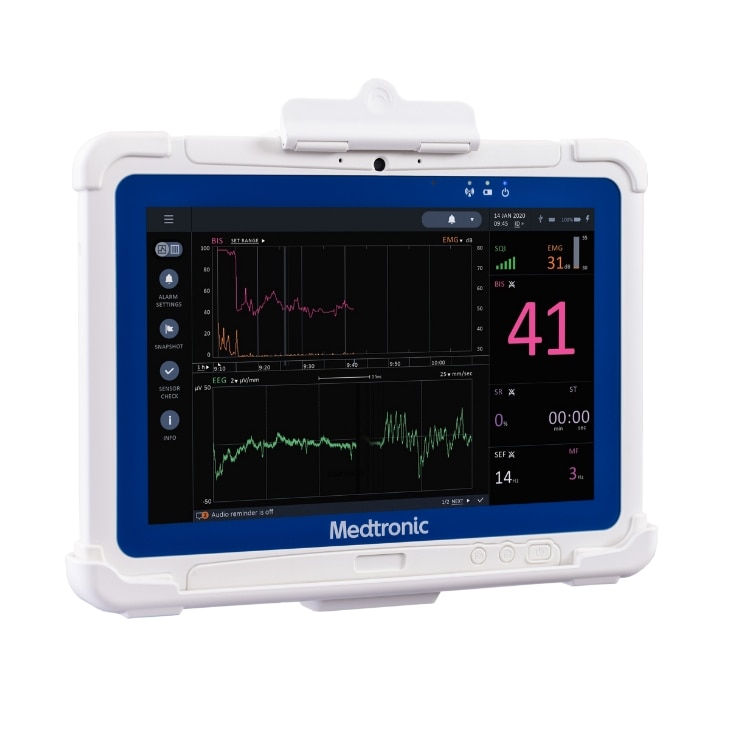
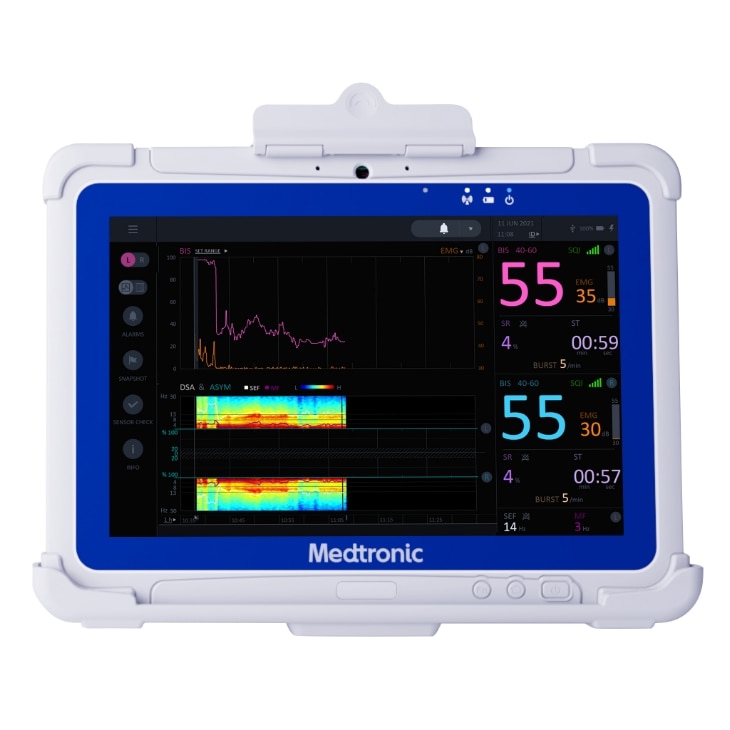
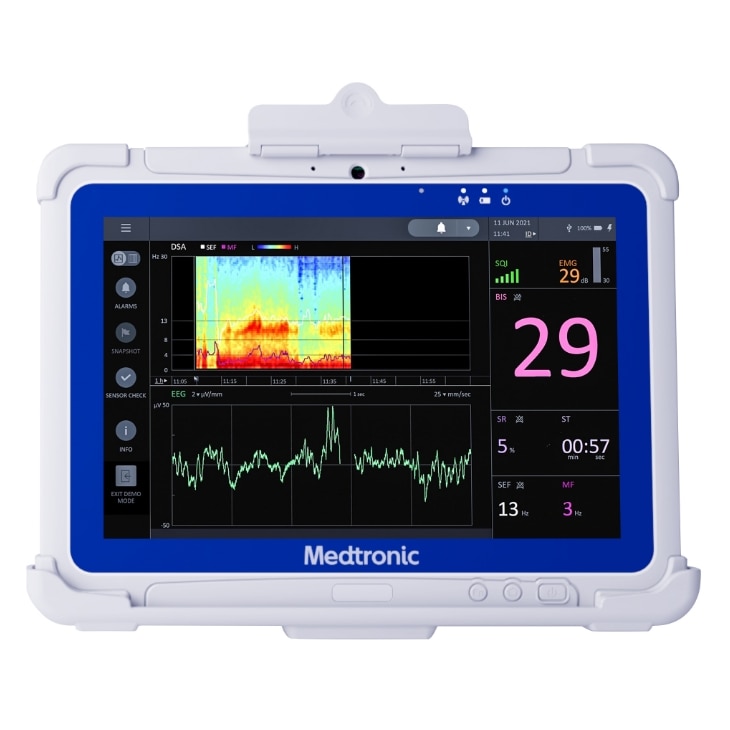
The BIS™ Advance is designed for a more efficient workflow.
Simple to read - through the large, high-resolution touchscreen monitor you can set system-wide default preferences to save time, as there is no need to re-set every time.
See the information you want - the configurable data and settings support you to save time with data output protocols that enable connectivity to Electronic Medical Records (EMRs).
Quickly review readings - the color-coordinated data enable you to maintain the continuous monitoring when moving between care settings.